A skipper should know how their boat will cope with rough seas. By working within known limits and understanding the risks, then the chances of a capsize occurring are much reduced.
Safety is all about improving the odds. When considering the odds of a boat capsizing, knowing the limitations of its design and stability are critical. In order to do this, it helps to understand the basic principles of how a boat remains upright.
Basic principles
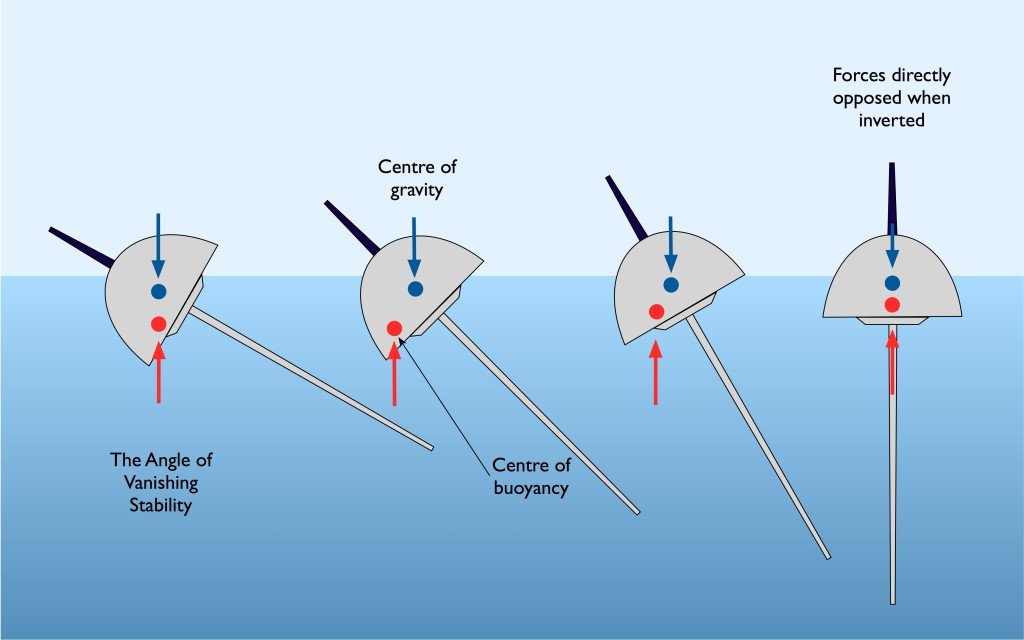
A boat remains upright because of the way its weight and buoyancy interact. The basic principle of buoyancy is that the upward buoyant force on a body immersed in fluid is equal and opposite to the weight of the fluid that the body displaces. The weight of the fluid displaced is known as displacement and the displaced water has an up thrust, or buoyancy, which is equal to the weight of the boat. The displaced water has a central point, or centre of buoyancy, which varies according to the shape of a boat’s hull and keel.
The centre of buoyancy is not to be mistaken for the centre of gravity. The weight of a boat is distributed along its length, pushing the entire vessel downwards. All the weight acts downwards through a central point, or centre of gravity, which is similar to the fulcrum or central point of a seesaw. All the structure and the distribution of weight aboard contribute to a boat’s centre of gravity.
To keep a boat stable in the water and prevent it from toppling over requires the centre of gravity to be low, which is greatly helped by having a deep, heavy keel and an engine below the waterline.
Angle of heel
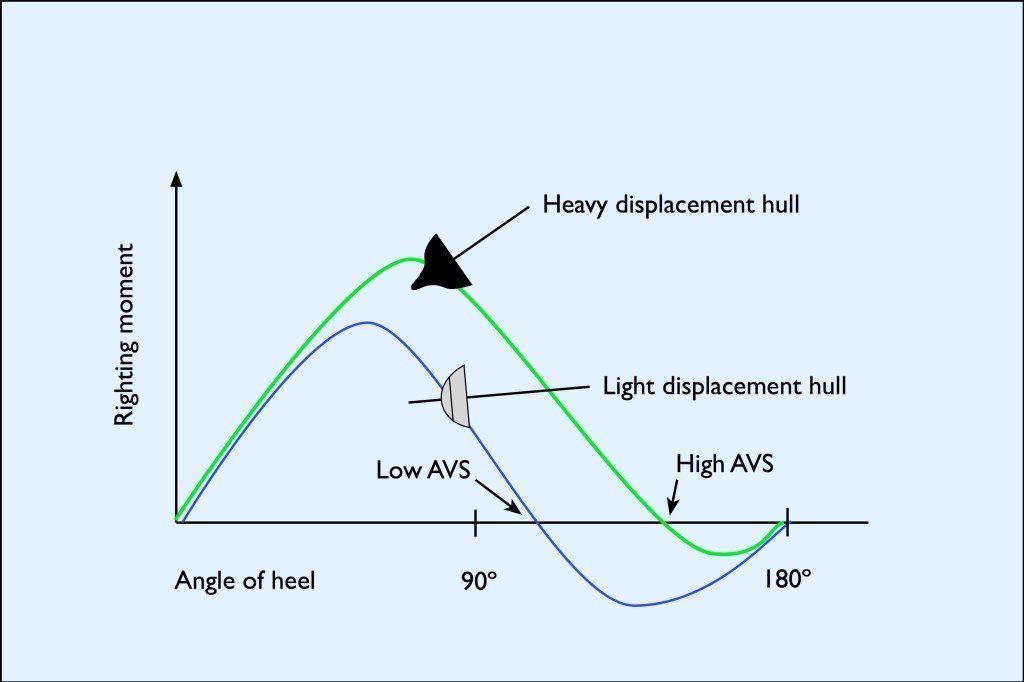
If a sailing boat heels over in a strong gust of wind or is forced over by a big wave, then it will right itself once the gust or wave has passed. When a boat is upright then the force of gravity is directly opposed to the force of buoyancy. As the boat heels over the centre of buoyancy moves outwards and acts as a lever does, pushing upwards with an increasing force. This is fine up to a point, but eventually as the boat continues to heel the righting lever effect reduces and eventually is lost and then the boat will capsize and float upside down. This point is known as the Angle of Vanishing Stability (AVS).
Boats with a high AVS will resist becoming inverted and return to the upright position quickly in the event of a knockdown. These include narrow, heavy displacement boats with a deep draft which can heel to 120º or more. Once capsized, only a small amount of further rolling moves the hull into the positive righting area and the boat comes back upright. Boats with wide beams and shallow drafts tend to have high initial stability but may capsize at 90º of heel and will not always be self-righting.
Righting moment curve
Boat manufacturers publish righting moment curves of their yachts to show the stability characteristics of their designs. In Europe the Recreational Craft Directive (RCD) states that pleasure yachts between 2.5m and 24m must carry builders’ plates to categorize their boats in either Category A (Ocean), B (Offshore) or C (Inshore) and meet minimum standards of stability.
Breaking waves
Rules and regulations are one thing, but the force of steep breaking waves can knock any yacht down in coastal waters, especially if it is caught beam-on. Research has shown that the most significant factor in capsize is whether a wave is breaking or not. If the wave is greater in height than the beam of the boat, then it can easily knock the boat over. Tests carried out at Southampton University in England have shown that almost any boat can be capsized by a wave equal to 55% of the boat’s overall length. Such waves may occur where the seabed suddenly shelves towards the coast, or where wind is blowing against tide.
This research points to the fact that yachts seeking shelter often find themselves in greater danger when approaching harbours than when coping with a storm further out to sea.
Being prepared
If you are well offshore in rough weather, consider your options. If needs be, heave to and ride out a storm as the boat will be more stable and comfortable, but check you have sufficient sea room to drift downwind and are not approaching a lee shore. Another option is to lie ahull, with no sail up and the helm tied to leeward. If conditions worsen then the next stage is to lie to a sea anchor or drogue, which will prevent the boat from meeting waves beam on and reduce the vessel’s drift rate.
Don’t automatically head for the nearest harbour or your intended destination. Check first what the conditions are likely to be there, by considering the state of the tide, wind direction and whether there are danger areas such as headlands and sand bars to contend with. Check out all the alternatives and be prepared to alter your plans in order to opt for a safe option.
Tips to prevent capsize:
- Know your boat’s limitations.
- Don’t overload the boat.
- Pump the bilges regularly.
- Keep a generous margin of safety.
- Know when it is best to yield to conditions, rather than fight them.
- Avoid areas known for overfalls and tide rips.
- Avoid being caught beam on to breaking waves.